A joint research team consisting of the Institute of Solid State Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Hefei Institute of Materials Science and the Strong Magnetic Field Science Center has made progress in the study of the transition metal dichalcogenide 2H-MoS2 ultrahigh-pressure. The research team used the diamond anvil high voltage generator to measure the superconductivity of 2Ha-MoS2 induced by high pressure through low-temperature electrical transport and synchrotron X-ray diffraction measurements. The density of the superconductivity microscopic view was calculated and explained. Mechanisms, related results are based on "2Ha-MoS2 superconductivity under ultra-high pressure," published in the "Physical Review Express", and was selected as the editorial recommended article. The transition metal dichalcogenide MX2 (M is a transition metal Ti, Nb, Ta, Mo, W; X is a chalcogen element S, Se, Te) has a layered structure similar to graphite, according to the XMX sandwich monolayer in the unit cell. The number of different MX6 coordination polyhedrons can be divided into 1T, 1T′, Td, 2H and other polymorphs. The ground states of electrons include charge density wave, Mote insulator, exciton insulator, semiconductor, semimetal, metal, and super. Guide and so on. Among them, metal 2H-NbS2, 2H-NbSe2, 2H-TaS2 and 2H-TaSe2 exhibited the behavior of charge density wave and superconductivity coexistence competition under normal pressure. Experimental studies have shown that the charge density wave transformation can be suppressed by chemical intercalation and the application of external pressure, thereby inducing superconductivity in the exciton insulator 1T-TiSe2 and the Mote insulator 1T-TaS2; furthermore, experimental studies have shown that there is no charge density In the outer ear half metal Td-WTe2 of the wave, superconductivity can also be induced by applying external pressure. The charge density wave transition of semiconductor 2Hc-MoS2 was not found under normal pressure. Experimentally, it was confirmed that superconductivity can be induced by chemical intercalation and electrostatic field bias. However, there is no experimental evidence of pressure induced superconductivity. Based on a self-built high-voltage comprehensive test platform, the research team found that the Ha-MoS2 superconductivity began to appear above 90 GPa, and the critical temperature of superconducting transition Tc was about 3K. As the pressure rises further, Tc increases sharply and reaches about 11K at about 120 GPa. Then, within the pressure range of 130 to 220 GPa, Tc remains unchanged at about 12K. High-voltage synchrotron x-ray diffraction measurements show that 2Ha-MoS2 has no structural phase transition, amorphization, or decomposition in the pressure range of 40-155GPa, indicating that superconductivity is the eigenstate of the 2Ha-MoS2 phase. The density functional calculations found that superconductivity can be attributed to the emergence of new hole-type Fermi pockets induced by high pressure in the 2Ha-MoS2 electronic structure. For the first time in this work, in the 2H structural transition metal dichalcogenide semiconductors with normal charge density waves, superconductivity was observed through pressure control studies, and the pressure-temperature phase diagram of transition metal dichalcogenide systems was enriched. The research work was supported by the national key R&D program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province. According to different methods of use, winches can be divided into four types: manual winches, electric winches, pneumatic winches, and hydraulic winches. At present, the largest marine hydraulic winch is 350T, and the weight of the equipment reaches 150T. Lifting And Traction Winch,Pneumatic Winches,Hydraulic Winches,Electric Winches Rugao Yaou Import & Export Trade Co., Ltd , https://www.ntyaou.com
Figure 1. Sample placement and electrode layout in a diamond to top anvil. 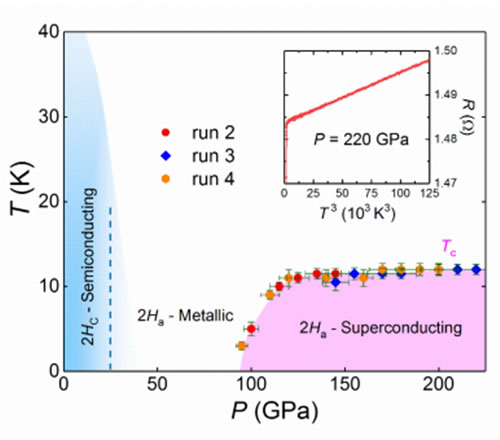
Fig. 2.2 Pressure-temperature phase diagram of H-MoS2.
According to the reel form, it is divided into single reel and double reel.
According to the reel distribution, there are parallel double reels and front and rear double reels.
The main technical indicators of hydraulic winches include rated load, supporting load, rope speed, rope capacity, etc.
A winch is a light and small lifting device (see hoisting machinery) that uses a reel to wind a wire rope or chain to lift or tow heavy objects, also known as a hoist. The winch can be used alone or as a component of machinery such as lifting, road construction and mine hoisting. It is widely used because of its simple operation, large rope winding volume and convenient displacement. The winch is also known as the hoist. The product has high versatility, compact structure, small size, light weight, heavy lifting, and convenient transfer. It is widely used in construction, water conservancy projects, forestry, mines, docks, etc. for material lifting or flat towing, and can also be used as modern electronic control Supporting equipment for automatic operation line.
According to the power, the winch is divided into three categories: manual, electric and hydraulic.
The transmission mechanism of the handle rotation of the manual winch is equipped with a stopper (ratchet wheel and pawl), which can keep the heavy object in the required position. The manual winch used for assembling or lifting heavy objects should also be equipped with safety handles and brakes. Manual winches are generally used in places where the lifting capacity is small, the facilities are poor, or where there is no power supply.
Electric winches are widely used in places with heavy work and large traction requirements. The electric motor of the single-drum electric winch (pictured) drives the drum through the reducer, and a brake is installed between the electric motor and the input shaft of the reducer. In order to meet the needs of lifting, traction and rotation, there are also double-drum and multi-drum winches. Generally, a winch with a rated load lower than 10T can be designed as an electric winch.
The hydraulic winch is mainly a winch with a larger rated load. Generally, the winch from 10T to 5000T is designed as a hydraulic winch. The winch can be divided into:
Marine winches: Marine winches can be divided into drag winches, mooring winches, anchor winches, traction winches, etc.
Engineering winch: Mainly used in engineering, with functions such as hoisting and hoisting as the main function.
Mine winches: divided into hoisting winches, dispatching winches, shaft sinking winches, column return winches, rake mine winches, column return winches, etc.
Cable winch: mainly used when laying cables.