Recently, Tang Yongbing, a researcher at the Functional Film Materials Research Center of the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, successfully developed a new type of zinc ion hybrid supercapacitor. This work has important implications for the study of novel energy storage devices based on polyvalent carriers. In order to alleviate the shortage of resources and environmental pollution caused by the massive use of fossil energy, various countries are accelerating the use of renewable energy such as solar energy, wind energy, water conservancy, and tidal energy. However, renewable energy has very obvious intermittent characteristics, and it needs to develop low-cost, high-efficiency energy storage technology to match it. Currently widely used lithium-ion batteries are an excellent electrochemical energy storage technology, but the reserves of lithium resources are very limited, and the distribution is extremely uneven, resulting in high cost of lithium-ion batteries, and recycling difficulties, limiting its large-scale Wide application of energy storage. The development of a new type of electrochemical energy storage device based on low cost and easy recovery has important research value and application prospects. Based on this, members of the Tang Yongbing team, Wang Heng and Wang Meng, developed a new type of high-efficiency, low-cost hybrid supercapacitor based on +2 zinc ions as active carriers. The device integrates an inexpensive zinc foil design and uses it as a negative electrode active material and current collector. The environmentally-friendly biomass activated carbon is used as the positive electrode, and the organic solvent containing the zinc salt is used as the electrolyte. The zinc ion is reduced at the negative electrode. The oxidation/reaction reaction and the adsorption/desorption reaction of anions on the positive electrode achieve reversible charging and discharging of the capacitor. The abundant zinc reserves, ion +2 price, can make zinc ion-based hybrid supercapacitors to obtain high energy density, while maintaining the advantages of low cost, easy recycling. After system optimization, this zinc ion hybrid supercapacitor achieved excellent electrochemical performance: at a power density of 1725 W/kg, the energy density was higher than 52 Wh/kg; and after 22,000 cycles, the capacity retention rate was higher than 91%. Large-scale energy storage in the field of renewable clean energy has a good application prospect. Related research results have been published on the Energy Storage Materials, a journal of energy storage materials, with the title A Novel Zinc-Ion Hybrid Supercapacitor for Long-Life and Low-Cost Energy Storage Applications. The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation, the Guangdong Science and Technology Plan Project, and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Plan Project. Dongguan Best Instrument Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.dgbestinstrument.com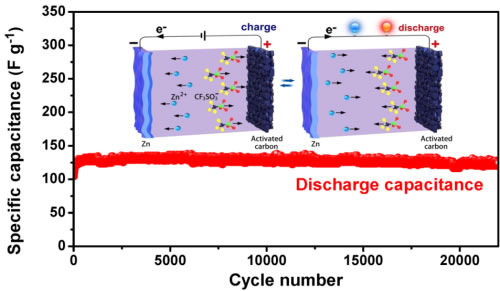
Structure and Reaction Mechanism of New Type Zinc Ion Hybrid Supercapacitor