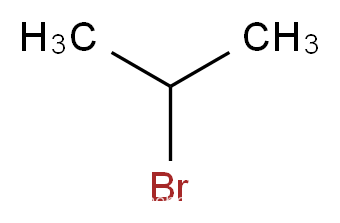Abstract: Puffing technology is a commonly used technology in modern feed processing. After the feed is processed by the expansion technology, the starch can be gelatinized and degraded in the feed, the protein is denatured, the anti-nutritional factor is lowered, and the palatability is increased. However, there are also disadvantages such as the formation of non-digestible substances, destruction of vitamins, and increase of cost. The article outlines the feed expansion technology and its advantages and disadvantages. Key words: puffing; advantages; shortcomings; feed 1 Puffing technology The puffing technology means that the material containing a certain amount of water is sent to the extrusion extruder. Under the action of the screw and the screw, the material moves axially forward, and the material and the spiral, the material and the barrel, and the mechanical friction inside the material. The material is strongly squeezed, stirred and sheared to further refine and homogenize the material, and then the internal pressure and temperature of the machine cavity are continuously increased and increased, and the material is under the action of high temperature, high pressure and high shear force. Complex material changes have occurred in the material components. Finally, the paste material is ejected from the die hole, and a pressure difference is instantaneously generated, and the material is expanded to form a loose, porous, crisp and puffed product, thereby achieving the purpose of extrusion. During the expansion process, the material has undergone great changes in texture, organization and appearance. The effect of material expansion is closely related to the technical parameters such as extrusion temperature, feed rate, raw material moisture, screw speed and die size. 2 Advantages of Puffing Technology After the puffing treatment, the feed material has a unique flavor and fluffy feeling, good palatability, high gelatinization degree and good attracting effect. At the same time, the long-chain structure of some organic substances such as proteins and fats becomes a short-chain structure, making it easier for animals to digest and absorb. 2.1 Starch gelatinization and degradation After extrusion and puffing, starch has undergone two major changes. First, the starch is gelatinized, and the bulking process disassembles the dense crystal structure of the starch molecules in the raw corn. The crystal structure begins to absorb the hydrolyzate, the hydrogen bond begins to break, and the expanded starch granules rupture and become a viscous melt. At the exit of the extruder, due to the sudden pressure drop, the steam is instantaneously lost, causing a large amount of expanded starch granules to disintegrate, and the starch is gelatinized to form a plurality of microporous expanded corn. On the other hand, starch degradation, the average molecular weight of starch is significantly reduced, and small molecular oligosaccharides such as maltodextrin can be produced by cleavage. Gelatinized starch has strong water absorption and a much stronger bonding function than ordinary starch, which can reduce the amount of starch used in production and provide more choices for other raw materials. Gelatinized starch binds protein tightly to the starch matrix to form a rumen non-degradable protein, a ruminal protein, which enhances the protein utilization of ruminants.
Product Name: N-propyl bromide ,1-Bromopropane
CAS NO.: 106-94-5
UN NO.: 2344
Hazard Class: 3.2
Molecular Formula: CH3CH2CH2Br
Chemical Formula:
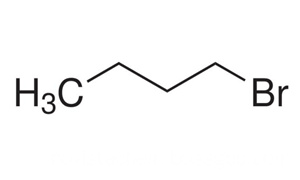
Product Name: N-butyl Bromide ; 1-Bromobutane
CAS NO.: 109-65-9
UN NO.: 1126
Hazard Class: 3
Molecular Formula: C4H9Br
Chemical Formula:
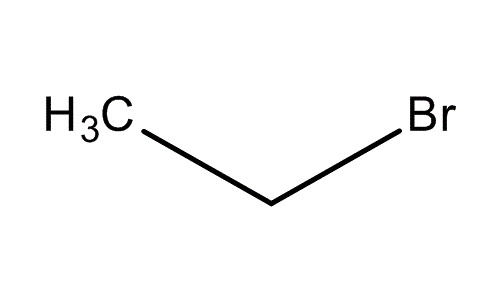
Product Name: Ethyl bromide ; Bromoethane
CAS NO.: 74-96-4
UN NO.: 1891
Hazard Class: 6.1
Molecular Formula: C2H5Br
Chemical Formula:
Product Name: Iso-propyl bromide ,2-Bromopropane
CAS NO.: 75-26-3
UN NO.: 2344
Hazard Class: 3.2
Molecular Formula: C3H7Br
Chemical Formula:
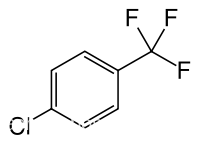
Product Name: P-chlorobenzotrifluoride (PCBTF)
Synonyms: 4-chlorobenzotrifluoride
CAS No: 98-56-6
M.F: C7H4CLF3
Un No: 2234
Imdg Class: 3
Chemical Formula:
Chemical Intermediate & Solvent Iso-Propyl Bromide IPB, N-Propyl Bromide NPB, P-chlorobenzotrifluoride PCBTF Shandong Novista Chemicals Co.,Ltd (Novista Group) , http://www.novistachem.com